Introduction
When it comes to digestive issues, one condition that can cause discomfort and serious complications is diverticulitis. Diverticulite sintomas can range from mild to severe, and understanding the early signs is crucial for timely treatment. This article will explore the key symptoms of diverticulitis, its causes, diagnosis, and treatment options. Whether you’re experiencing symptoms or simply want to stay informed, this guide provides easy-to-understand information to help you.
What Is Diverticulitis?
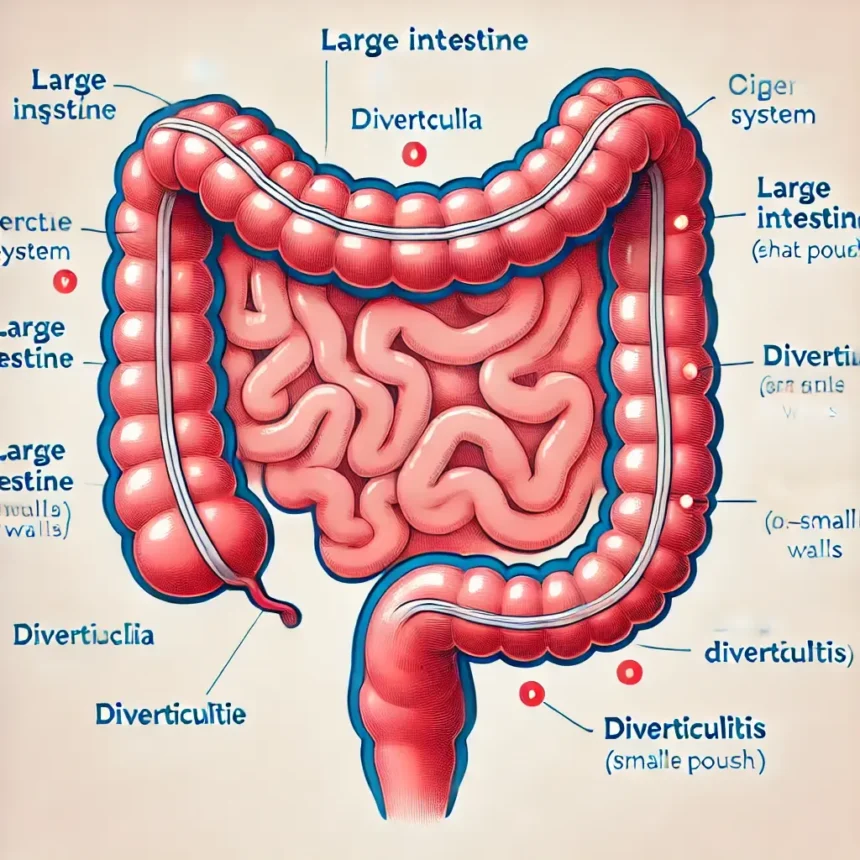
Diverticulitis is a condition where small, bulging pouches called diverticula form in the digestive tract, particularly in the colon (large intestine). When these pouches become inflamed or infected, it leads to diverticulitis. The condition can result in intense pain and complications, such as infections or blockages in the intestine.
Diverticulite Sintomas: Key Symptoms to Look Out For
Diverticulitis has distinct symptoms, but they can vary from person to person. Here are the most common diverticulite sintomas:
- Abdominal Pain
The most common symptom of diverticulitis is persistent, intense pain, usually felt in the lower left side of the abdomen. The pain may worsen over time or come in waves. - Fever
A mild fever often accompanies diverticulitis, indicating the presence of an infection. If the fever persists or increases, medical attention may be necessary. - Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are frequent symptoms associated with diverticulitis, especially when the condition becomes more severe. These symptoms arise due to the body’s response to inflammation in the digestive system. - Constipation or Diarrhea
Changes in bowel habits are common, with some people experiencing constipation while others may have diarrhea. These changes are due to the inflamed diverticula affecting normal digestion. - Bloating and Gas
Many individuals with diverticulitis feel bloated or gassy, as their digestive system struggles to process food effectively due to the inflammation. - Blood in Stool
Although not always present, some individuals may notice blood in their stool, which is a sign of more severe diverticulitis or complications.
What Causes Diverticulitis?
The exact cause of diverticulitis isn’t always clear, but there are several known risk factors that contribute to the development of diverticula and their inflammation. These include:
- Age: The risk of diverticulitis increases as you age, with most cases occurring in people over 40.
- Low Fiber Diet: A diet low in fiber leads to harder stools, which can increase pressure in the colon and contribute to the formation of diverticula.
- Lack of Exercise: Regular physical activity helps maintain healthy digestion, reducing the risk of diverticulitis.
- Obesity:Having a higher weight or living in a higher-weight body is linked to an increased risk of diverticulitis.
- Smoking: Smoking can affect digestive health and increase the likelihood of inflammation in the colon.
Diagnosis of Diverticulitis
If you’re experiencing diverticulite sintomas, a healthcare provider will likely perform a physical examination and ask about your symptoms. They may recommend one or more diagnostic tests, such as:
- CT Scan: This is the most common test used to diagnose diverticulitis. It provides detailed images of the colon and can show any inflammation or complications.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can reveal signs of infection or inflammation in the body.
- Colonoscopy: In some cases, a colonoscopy may be recommended after recovery to assess the overall health of the colon.
Treatment Options for Diverticulitis
Treatment for diverticulitis varies depending on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, home treatments may be sufficient, while more severe cases may require medical intervention.
- Home Treatment for Mild Cases
- Rest: Resting your body gives it time to recover and heal.
- Liquid Diet: A temporary liquid diet helps reduce stress on the digestive system while it heals.
- Antibiotics: If an infection is present, a doctor may prescribe antibiotics to fight the infection.
- Medical Treatment for Severe Cases
- Hospitalization: In more severe cases, you may need to be hospitalized for intravenous antibiotics and fluids.
- Surgery: If diverticulitis leads to complications such as abscesses, blockages, or perforations in the colon, surgery may be required to remove the damaged sections of the intestine.
Complications of Diverticulitis
While most cases of diverticulitis are treatable, the condition can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Potential complications include:
- Abscess: An abscess is a collection of pus that can form around the inflamed diverticula.
- Perforation: In rare cases, the diverticula can tear, causing a hole in the colon and leading to infection in the abdominal cavity (peritonitis).
- Fistula: A fistula is an abnormal connection between two organs, often occurring between the colon and bladder or other nearby structures.
- Bowel Obstruction: Inflammation can cause a blockage in the intestines, preventing the passage of stool and leading to severe pain and complications.
Preventing Diverticulitis
While it may not be possible to completely prevent diverticulitis, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Increase Fiber Intake
Eating a diet rich in fiber helps promote regular bowel movements and prevents the formation of diverticula. Include foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet. - Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water keeps stools soft, making them easier to pass and reducing the pressure on the colon. - Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity helps improve digestion and reduce the risk of constipation. - Avoid Smoking
Quitting smoking can improve overall digestive health and reduce inflammation in the colon.
FAQs
1. What is the most common symptom of diverticulitis?
The most common symptom of diverticulitis is persistent abdominal pain, often located on the lower left side of the abdomen.
2. Can diverticulitis go away on its own?
Mild cases of diverticulitis can improve with home treatment, including rest and dietary changes. However, it’s essential to seek medical attention if symptoms worsen.
3. How is diverticulitis diagnosed?
A healthcare provider may use a CT scan, blood tests, or a colonoscopy to diagnose diverticulitis.
4. Is diverticulitis a serious condition?
Diverticulitis can become serious if left untreated, leading to complications such as abscesses, perforations, or bowel obstructions.
5. What foods should I avoid if I have diverticulitis?
During a flare-up, it’s best to avoid hard-to-digest foods like nuts, seeds, and popcorn. A liquid diet may be recommended to give the digestive system a break.
Conclusion
Diverticulitis can be a painful and disruptive condition, but with the right treatment and lifestyle changes, it is manageable. Recognizing diverticulite sintomas early and seeking appropriate medical care is key to preventing complications. By adopting a fiber-rich diet, staying hydrated, and maintaining an active lifestyle, you can reduce your risk of developing diverticulitis and improve your digestive health.