Introduction
The camel spider is a unique arachnid that captures people’s attention due to its size and rumors surrounding it. While often misunderstood, the camel spider is a fascinating creature with characteristics that make it unique among arachnids. From its unusual habitat to its behavior, this creature deserves a closer look. This article aims to explore everything about the camel spider, offering a clear and accessible guide for the average reader.
Table of Contents
- What is a Camel Spider?
- The Habitat of Camel Spiders
- Physical Characteristics of Camel Spiders
- Camel Spider Myths and Facts
- Camel Spider Behavior and Diet
- Are Camel Spiders Dangerous?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is a Camel Spider?
The camel spider, also known as Solifugae, is a type of arachnid that belongs to its own distinct order. Camel spiders are not actually spiders, nor are they scorpions, though they are closely related to both. They are unique creatures with fascinating attributes that make them stand out. The term “camel spider” often causes confusion, as people might assume they are either spiders or have a direct association with camels.
Despite common myths, camel spiders do not feed on camels. The name “camel spider” likely comes from their presence in deserts, often near camel habitats. The camel spider is primarily found in arid regions around the world, including North Africa, the Middle East, and parts of the United States.
The Habitat of Camel Spiders
Camel spiders thrive in hot, dry environments, as their natural habitat is the desert. These creatures are found in regions with extreme temperatures, such as North Africa, the Middle East, and the southwestern United States. Desert conditions suit camel spiders due to their ability to adapt to minimal water intake and high temperatures.
Despite their preference for dry areas, camel spiders seek out shade during the hottest parts of the day. They often hide under rocks, burrow in the sand, or seek shelter under objects to avoid the sun. During the night, they become more active, which is why they are often called “nocturnal hunters.”
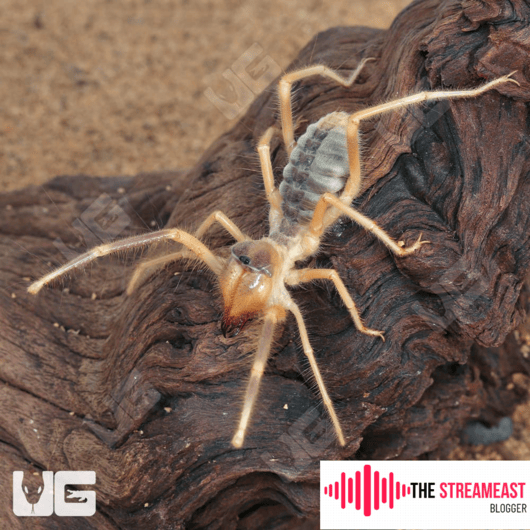
Physical Characteristics of Camel Spiders
Camel_spiders are known for their large size and unique physical attributes. On average, camel_spiders can grow up to 6 inches long, including their legs. Their body is divided into two main sections, like other arachnids: the cephalothorax (head and thorax combined) and the abdomen.
Their bodies are covered in sensory hairs that help them navigate and sense their environment. Camel_spiders have strong, forward-pointing jaws called chelicerae, which they use for hunting and tearing apart prey. These jaws are particularly intimidating and are often the source of myths about the camel_spider’s dangerousness.
Despite their fearsome appearance, camel_spiders have a natural coloration that helps them blend into the desert environment. Their color ranges from light brown to dark tan, allowing them to camouflage easily in sandy landscapes.
Camel Spider Myths and Facts
The camel_spider has become a subject of many myths, often due to exaggerations on the internet and sensationalized stories. Below are some common myths about camel_spiders and the truths behind them.
Myth 1: Camel Spiders Are Deadly to Humans
One of the biggest myths about camel_spiders is that they are deadly to humans. In reality, camel_spiders do not have venom that can harm humans. While they can deliver a painful bite, it is not life-threatening.
Myth 2: Camel Spiders Can Run as Fast as a Human
Another myth is that camel_spiders can chase humans at incredible speeds. While they are indeed fast, reaching speeds of up to 10 miles per hour, they are not capable of outrunning a human.
Myth 3: Camel Spiders Eat Camels
This is one of the most absurd myths about camel_spiders. Camel_spiders do not feed on camels or any large animals. They primarily hunt insects and small animals.
These myths often cause people to fear camel_spiders unnecessarily. Understanding the reality about these arachnids can help dispel irrational fears and appreciate them for their unique role in the ecosystem.
Camel Spider Behavior and Diet
Camel_spiders are active hunters, known for their aggressive hunting style. Unlike many spiders that rely on webs, camel_spiders hunt for their prey by stalking and pouncing on it. They are nocturnal, becoming active during the night to avoid the heat of the desert sun.
Camel_spiders primarily feed on insects, small rodents, lizards, and other small animals. Their strong jaws allow them to crush their prey and eat it efficiently. Camel_spiders are also known to scavenge if they come across a food source, though they prefer to hunt live prey.
Interestingly, camel_spiders are not venomous, which makes them different from many spiders. They rely on their strong jaws to subdue their prey rather than venom. This hunting style makes them unique among arachnids.
Are Camel Spiders Dangerous?
While camel_spiders may look intimidating due to their size and jaws, they are not dangerous to humans. They are not venomous and do not pose a threat to people. However, their bite can be painful, and they may bite if they feel threatened. In most cases, camel_spiders will avoid humans and try to escape if encountered.
Camel_spiders can be beneficial as they help control insect populations in desert environments. Their presence can be a positive aspect of the desert ecosystem, contributing to the natural balance by hunting small pests.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the scientific name for the camel_spider?
The camel_spider belongs to the order Solifugae, which encompasses multiple species.
2. Are camel_spiders venomous?
No, camel_spiders are not venomous. They rely on their strong jaws to hunt rather than venom.
3. Where do camel_spiders live?
Camel_spiders are typically found in desert regions, including North Africa, the Middle East, and southwestern parts of the United States.
4. Do camel_spiders really chase humans?
Camel_spiders may appear to chase humans, but they are likely seeking shade rather than attacking.
5. How fast can a camel_spider run?
Camel_spiders can run up to 10 miles per hour, making them fast hunters in the desert.
6. Can a camel_spider harm a camel?
No, camel_spiders do not harm camels. They feed on insects and small animals, not large mammals.
7. Are camel_spiders related to true spiders?
Camel_spiders are arachnids, like true spiders, but they belong to a different order, Solifugae.
8. Why are camel_spiders called “camel_spiders”?
The name likely comes from their presence in desert areas where camels are found, though they have no direct relation to camels.
9. How do camel_spiders protect themselves from the heat?
Camel_spiders hide in burrows or under rocks during the day to avoid the sun’s heat.
10. What do camel_spiders eat?
Camel_spiders eat insects, small rodents, and other small animals in their environment.
Conclusion
Camel_spiders are an interesting and misunderstood group of arachnids. Though they have a fearsome reputation, much of this is based on myths and exaggerations. In reality, camel_spiders play an important role in the desert ecosystem by controlling insect populations. Their unique physical characteristics and hunting style make them a fascinating creature worth understanding.