Introduction
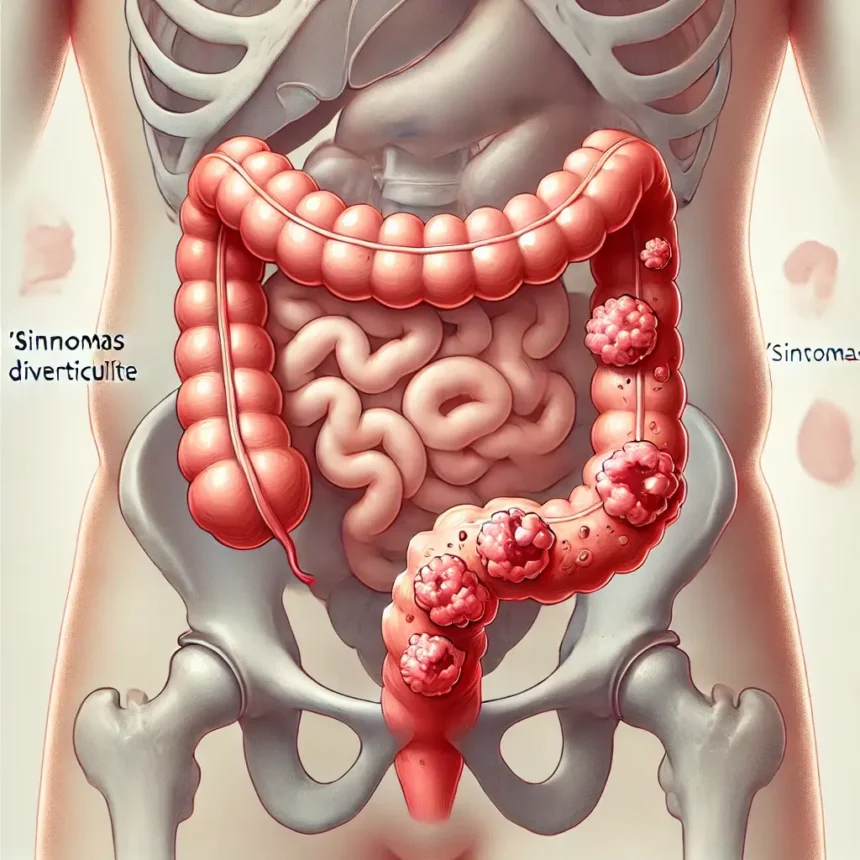
Diverticulitis is a condition that affects the digestive system, specifically the large intestine (colon). It occurs when small, bulging pouches called diverticula form along the walls of the colon and become inflamed or infected. The symptoms of diverticulitis can vary from mild discomfort to severe complications. In this article, we will discuss the most common “sintomas de diverticulite” in easy-to-understand language, so you can identify and understand this condition better.
What is Diverticulitis?
Before diving into the “sintomas de diverticulite,” it’s essential to understand what diverticulitis is. Diverticula are small pouches that can form in weak spots along the digestive tract, particularly in the colon. When these pouches become inflamed or infected, the condition is known as diverticulitis. While diverticula can exist without causing any problems (a condition known as diverticulosis), diverticulitis is more severe and can lead to significant health issues if left untreated.
Sintomas de Diverticulite
The symptoms of diverticulitis can range from mild to severe and usually depend on the severity of the inflammation or infection. It is crucial to recognize the early signs of this condition to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
1. Abdominal Pain
One of the most common “sintomas de diverticulite” is abdominal pain. This pain is usually felt on the lower left side of the abdomen but can occur in other areas as well. The pain can be sudden and severe or develop gradually over a few days. The discomfort often worsens after eating or when moving, and some people may find relief after passing gas or having a bowel movement.
2. Fever and Chills
Fever and chills are other typical “sintomas de diverticulite.” These symptoms occur when the body tries to fight off the infection or inflammation in the colon. A fever higher than 100.4°F (38°C) is a sign that the diverticulitis may be worsening, and it’s essential to seek medical care if this occurs.
3. Changes in Bowel Habits
Diverticulitis can lead to changes in your usual bowel habits. This can include constipation or diarrhea, both of which are common “sintomas de diverticulite.” Some people may experience difficulty passing stool or notice that their stool has become loose and watery. These changes can also be accompanied by a feeling of incomplete evacuation after using the bathroom.
4. Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are additional “sintomas de diverticulite” that can occur due to the inflammation in the colon. The discomfort and irritation in the digestive system can lead to feelings of nausea, and in more severe cases, vomiting may also occur.
5. Bloating and Gas
Many individuals with diverticulitis report feeling bloated or gassy. The trapped gas in the colon due to the inflammation can cause uncomfortable bloating. This sensation may be more pronounced after eating, especially if the diet is high in fiber, which can further irritate the inflamed pouches.
6. Blood in Stool
Blood in the stool is a more serious “sintomas de diverticulite” and should not be ignored. This can indicate that the diverticula are bleeding, which can be a sign of a complication. The blood may appear bright red or dark, depending on its location in the colon. If you notice blood in your stool, seek medical attention immediately.
7. Tenderness in the Abdomen
Along with abdominal pain, tenderness in the abdomen is a common “sintomas de diverticulite.” Pressing on the affected area can cause discomfort or pain. This tenderness usually occurs on the left side of the abdomen but can occur elsewhere depending on the location of the diverticula.
8. Fatigue
The body’s response to infection or inflammation often leads to fatigue. Feeling unusually tired, weak, or lacking energy is a frequent “sintomas de diverticulite.” This is because your body is working hard to fight off the inflammation or infection in the colon, which can drain your energy levels.
How to Manage Sintomas de Diverticulite
Managing the symptoms of diverticulitis largely depends on the severity of the condition. Mild cases of diverticulitis can often be treated at home with rest, dietary changes, and medications. Here are some common management strategies:
1. Rest
One of the most important things you can do when experiencing “sintomas de diverticulite” is to rest. Resting allows your body to heal and reduces the strain on your digestive system.
2. Antibiotics
If an infection is present, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to help clear the infection and reduce inflammation. It’s crucial to follow the full course of antibiotics, even if you start feeling better before the medication is finished.
3. Dietary Changes
During a flare-up of diverticulitis, your doctor may recommend a liquid or low-fiber diet to give your colon time to heal. Once the symptoms improve, you can gradually return to a normal diet. It’s essential to include plenty of fiber in your diet to help prevent future flare-ups.
4. Pain Relief
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen, can help relieve mild discomfort. However, avoid nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or aspirin, as they can irritate the colon and worsen the condition.
5. Surgery
In more severe cases of diverticulitis, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected portion of the colon. This is usually only considered when other treatments have failed or if complications, such as abscesses or perforations, have occurred.
FAQs
What are the first symptoms of diverticulitis?
The first symptoms of diverticulitis are usually abdominal pain, especially on the lower left side, and changes in bowel habits like constipation or diarrhea.
Can diverticulitis go away on its own?
Mild cases of diverticulitis may improve with rest, dietary changes, and medications. However, more severe cases require medical treatment to prevent complications.
Is diverticulitis a serious condition?
While mild diverticulitis can be managed with proper care, severe cases can lead to complications like abscesses, perforation of the colon, or peritonitis, which can be life-threatening.
How long do the symptoms of diverticulitis last?
The duration of diverticulitis symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Mild cases may improve within a few days, while more severe cases can take weeks to resolve.
Can diverticulitis be prevented?
You can reduce your risk of developing diverticulitis by eating a high-fiber diet, drinking plenty of water, and staying physically active. Fiber helps keep your bowel movements regular, reducing pressure on the colon and preventing the formation of diverticula.
Conclusion
Understanding the “sintomas de diverticulite” is essential for recognizing the condition early and seeking appropriate treatment. While diverticulitis can be mild in some cases, it can also lead to severe complications if not treated properly. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, especially persistent abdominal pain or blood in your stool, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider. Early intervention can help prevent the condition from worsening and improve your quality of life.